Why Is Leukemia So Fatal? Unpacking The Serious Nature Of Blood Cancers
When someone mentions leukemia, a sense of deep worry often comes over people, and for good reason. It’s a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, and it can be incredibly serious, really, very much so. Many people wonder, quite naturally, why this particular illness can be so dangerous, leading to such difficult outcomes for those who face it.
You see, unlike some other cancers that might form a solid mass, leukemia is a bit different. It spreads through the body's very own liquid systems, making it, in a way, harder to contain. This means its reach can be wide, and its effects on the body's essential functions can be profound, pretty quickly, too.
So, we're going to talk about the main reasons why leukemia can be such a life-threatening condition. We'll look at how it starts, what it does inside the body, and why it can be so hard to get rid of, even with today's medical advancements. It's important, you know, to understand these things.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Leukemia: A Serious Blood Cancer
- Why Leukemia Cells Cause Such Harm
- The Challenge of Early Detection and Swift Progression
- Treatment Hurdles and Complications
- The Risk of Relapse
- The Body's Struggle and Ongoing Research
- Frequently Asked Questions About Leukemia's Severity
- Seeking Support and Staying Informed
Understanding Leukemia: A Serious Blood Cancer
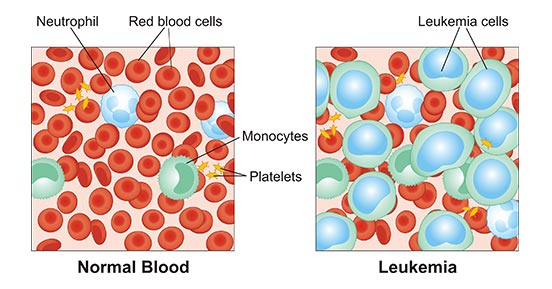
Leukemia, at its core, is a cancer that starts in the blood-forming tissues of the body, like the bone marrow. This is where all our blood cells are made, you know, the red ones, the white ones, and the platelets. Normally, these cells grow and mature in a very controlled way, each doing its specific job, and stuff.
But with leukemia, something goes wrong with this careful process. Instead of making healthy, working blood cells, the body starts producing a huge number of abnormal white blood cells. These bad cells don't mature properly, and they can't do the jobs that healthy white blood cells are supposed to do, like fighting off sickness. It's a bit like a factory suddenly making only faulty parts, and those parts just keep piling up, as a matter of fact.
What Happens in Leukemia
Basically, leukemia happens when the DNA of a single blood-forming cell gets damaged. This damage makes the cell grow and divide without stopping, unlike normal cells that know when to quit. These abnormal cells, often called "blasts," don't mature into proper working blood cells, which is a real problem, obviously.
They multiply very quickly, especially in acute forms of the illness, filling up the bone marrow. This crowding out means there's less space for the body to make the good, healthy blood cells it desperately needs. So, you end up with too many bad cells and not enough good ones, which is pretty serious.
This unchecked growth can happen quite fast, leading to a rapid decline in a person's health. It's not just about having "cancer cells"; it's about these specific cells taking over the very system that keeps your body running, which, you know, is really important.
The Different Kinds
There are a few main types of leukemia, and they act a bit differently, actually. They are generally grouped by how quickly they progress and which type of white blood cell they affect. Acute leukemias, for example, tend to come on very suddenly and get worse quickly, requiring immediate attention, seriously.
Chronic leukemias, on the other hand, might grow slowly for a long time, sometimes without many obvious signs at first. Then there are myeloid leukemias and lymphoid leukemias, which refer to the specific type of immature white blood cell that turns cancerous. Each type, you know, presents its own set of challenges.
The type of leukemia a person has plays a big role in how it behaves and what kind of approach doctors will take to try and fight it. Some forms are, arguably, more aggressive than others, making the situation even more urgent for patients and their families.
Why Leukemia Cells Cause Such Harm
The core issue with leukemia, really, is that these abnormal cells don't just sit there. They actively interfere with the body's ability to make healthy blood components. This disruption has widespread consequences because blood, as you know, carries oxygen, fights infections, and helps stop bleeding, and so on.
When the bad cells take over, the body simply can't perform these basic, life-sustaining tasks properly. It's like a vital part of your body's support system is being slowly, or sometimes quickly, choked off. This is why the illness can be so dangerous, pretty much.
Overwhelming the System
The bone marrow, which is like the blood cell factory, gets completely filled up with these faulty leukemia cells. They don't just stay in the marrow; they can spill out into the bloodstream and travel throughout the body, honestly.
This means they can start to collect in other organs, like the spleen, liver, and lymph nodes, causing them to swell or not work right. In some cases, they can even get into the brain and spinal cord, creating even more serious problems. This spread makes it incredibly difficult to target all the bad cells, you know.
The sheer number of these non-functional cells means there's simply no room, and no resources, for the body to make the good cells it needs. It's a bit like a garden being completely overgrown with weeds, leaving no space for the valuable plants to grow, basically.
Impact on Vital Functions
When healthy blood cells are pushed aside, a person's body starts to struggle in many ways. This lack of proper blood cells leads to a cascade of problems that can quickly become life-threatening, pretty serious ones, too.
For instance, not enough red blood cells leads to anemia. This means your body isn't getting enough oxygen, which can make you feel incredibly tired, weak, and short of breath. It's like trying to run a car on very little fuel, which, you know, just won't work well.
Then there's the problem with white blood cells. While leukemia involves too many white blood cells, these are the wrong kind. They can't fight off infections effectively, leaving the person very vulnerable to even common germs. A simple cold can become a very serious, life-threatening situation, as a matter of fact.
And platelets, which help your blood clot, also become scarce. This means a person with leukemia can bruise very easily, bleed from their gums or nose, or even have serious internal bleeding. This risk of uncontrolled bleeding is, quite frankly, a major danger.
The Challenge of Early Detection and Swift Progression
One of the tricky things about leukemia is that its initial signs can be very general and easy to miss, particularly in the beginning. People might just feel tired or run down, which could be put down to many other things, honestly.
This means that sometimes, by the time someone realizes something is really wrong, the disease has already had a chance to become quite advanced. It's not always like a clear warning bell going off, you know.
Subtle Beginnings
The early signs of leukemia can often mimic other less serious illnesses, like the flu or a common infection. Things like feeling weary, having a low fever, or just not feeling quite right can be dismissed as everyday ailments, and stuff.
Because these signs are so vague, it can take a little while for doctors to figure out what's truly going on. This delay, even a short one, can be very significant, especially for the fast-moving types of leukemia, as you might imagine.
Rapid Onset
For acute leukemias, the progression from feeling okay to being very sick can happen incredibly fast. We're talking about weeks or even just days, in some cases. This rapid worsening is a major reason why it's so serious, absolutely.
The body just doesn't have time to adapt, and the systems quickly become overwhelmed. This swift, aggressive nature means that treatment needs to start very, very quickly once the diagnosis is made, which, you know, adds to the pressure.
Treatment Hurdles and Complications
Fighting leukemia often involves very strong and intense medical approaches. These methods are designed to kill the fast-growing cancer cells, but they can also cause significant harm to the body's healthy cells, too, unfortunately.
This balance between wiping out the bad cells and keeping the person strong enough to survive the process is a constant, difficult challenge. It's a very fine line to walk, as a matter of fact.
Aggressive Therapies
Chemotherapy is a common way to fight leukemia, using powerful medicines to destroy cancer cells. But these medicines also hit fast-growing healthy cells, like those in the hair, mouth, and gut, and especially the healthy blood-forming cells in the bone marrow, seriously.
This can lead to severe side effects such as extreme tiredness, nausea, hair loss, and a greatly weakened immune system. The body becomes very fragile during this time, which is, you know, incredibly tough for the person going through it.
Sometimes, radiation therapy is also used, which uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. While targeted, it too can cause damage to healthy tissues and contribute to the overall strain on the body. It's a really intense process, basically.
Resistance to Treatment
A significant problem with leukemia is that the cancer cells can sometimes develop ways to resist the medicines meant to kill them. This means the treatment that worked at first might stop being effective, which is very frustrating, obviously.
When cells become resistant, doctors have to try different, sometimes even stronger, combinations of medicines, or look for other ways to fight the disease. This can make the whole process much longer and harder on the person, and stuff.
It's like the cancer cells are learning to outsmart the very drugs designed to eliminate them, which, you know, makes the fight even more complicated and difficult for everyone involved.
The Complexity of Transplants
For many people with leukemia, a stem cell transplant, sometimes called a bone marrow transplant, offers the best chance for a long-term recovery. This involves replacing the diseased bone marrow with healthy blood-forming stem cells, usually from a donor, or sometimes from the person themselves, if possible.
However, this is a very complex and risky procedure. Before the transplant, the person has to go through very high doses of chemotherapy or radiation to destroy their own bone marrow, which is, honestly, incredibly hard on the body.
After the transplant, there's a risk of serious complications, like graft-versus-host disease, where the new cells attack the person's body. It's a long recovery period, and the body's immune system is severely compromised for a long time, making infections a constant threat, seriously.
Infections and Bleeding
Because leukemia itself, and its treatments, severely reduce the number of healthy white blood cells and platelets, people with leukemia are at a very high risk of serious infections and uncontrolled bleeding. These complications are, in a way, often the direct cause of death, rather than the cancer itself, sometimes.
A simple bacterial or fungal infection that a healthy person would easily fight off can become life-threatening for someone with a weakened immune system. Doctors have to be very, very careful and constantly monitor for any signs of infection, you know.
Similarly, the lack of platelets means even a small cut or internal bruise can lead to significant blood loss. Managing these risks is a constant and vital part of caring for someone with leukemia, pretty much.
The Risk of Relapse
Even after successful treatment, there's always the concern that leukemia might come back. This is called a relapse, and it's a very real worry for many who have gone through treatment, as a matter of fact.
The reason for this is that some leukemia cells can survive the initial treatment, even if they are very few. These "hiding" cells can then start to multiply again, causing the disease to return, which is incredibly disheartening, obviously.
Hiding Cells
It's incredibly difficult for treatments to wipe out every single cancer cell in the body. Some cells might be in places that medicines don't reach as well, or they might be in a dormant state, making them less vulnerable to chemotherapy, you know.
These few surviving cells can then, over time, begin to grow and divide again, leading to a recurrence of the disease. It's like trying to get rid of every single weed in a garden; a few tiny seeds might remain, ready to sprout again, basically.
More Difficult to Treat
When leukemia comes back, it can often be even harder to treat than the first time. The cells that survived the initial treatment might have become resistant to those drugs, meaning new, different, and often stronger approaches are needed, seriously.
This can mean more intense chemotherapy, different types of targeted therapies, or another stem cell transplant, if possible. Each relapse adds to the physical and emotional toll on the person, and the chances of a lasting recovery can become slimmer, unfortunately.
The Body's Struggle and Ongoing Research
At the end of the day, leukemia is so fatal because it directly attacks the body's lifeblood and its ability to defend itself. The body simply gets overwhelmed by the sheer number of abnormal cells and the resulting lack of healthy ones, which, you know, is a dire situation.
The continuous strain on the organs, the constant risk of infection, and the severe side effects of the necessary treatments all contribute to the high fatality rate. It's a relentless battle for the body, pretty much.
Overwhelmed Defenses
Our immune system is designed to protect us from harm, but with leukemia, it's essentially fighting a losing battle from within. The very cells that are supposed to be the defenders become the problem, and they outnumber the healthy ones, which is a major issue.
This means the body can't mount an effective defense against the cancer itself, nor can it protect against outside threats like bacteria and viruses. It's like your body's security system has been completely taken over by the intruders, you know.
Hope Through Science
Even with all these serious challenges, there's a lot of incredible work being done in the medical world right now. Researchers are constantly looking for better ways to understand and fight leukemia, which is, honestly, very encouraging.
New targeted therapies, for instance, are being developed that aim to attack only the cancer cells, leaving healthy cells mostly untouched. Immunotherapies, which help a person's own immune system recognize and fight the cancer, are also showing a lot of promise, as a matter of fact. As of today, scientists are making strides in understanding the genetic makeup of different leukemias, which could lead to even more personalized and effective treatments in the future, seriously.
These advancements, you know, offer a lot of hope that one day, leukemia might not be as fatal as it is now. There's still a long way to go, but the dedication to finding cures is absolutely there.
Frequently Asked Questions About Leukemia's Severity
Is leukemia always a death sentence?
No, definitely not always. While leukemia can be very serious, many people, especially children, achieve long-term remission or are cured. Survival rates have improved a lot over the years, thanks to better treatments and earlier detection, you know. It really depends on the type of leukemia, how early it's found, and how a person responds to the different ways doctors try to fight it.
What are the first signs of leukemia that make it so dangerous?
The early signs can be pretty vague, making them dangerous because they can be missed. Things like feeling very tired, having fevers, losing weight without trying, or getting frequent infections are common. Also, easy bruising or bleeding can be a sign. Because these are not specific, it can delay getting the right diagnosis, which, for a fast-moving illness, can be a real problem, honestly.

Types of Cancer - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Risk Factors

Leukemia (Blood Cancer) - Symptoms & Causes | Gleneagles Hospital
Leukemia, Why is it So Common?